A startup means an entity, incorporated or registered in India, not before five years, with an annual turnover not exceeding INR 25 crore in any preceding financial year, working towards innovation, development, deployment, or commercialization of new products, processes, or services driven by technology or intellectual property.
Provided that such entity is not formed by splitting up, or reconstruction, of a business already in existence. Provided also that an entity[1] shall cease to be a Startup if its turnover for the previous financial years has exceeded INR 25 crore or it has completed 5 years from the date of incorporation/ registration. Provided further that a Startup shall be eligible for tax benefits only after it has obtained certification from the Inter-Ministerial Board[2], set up for the such purpose.
The broad scope of Startup India’s programs is outlined and is managed by a dedicated Startup India Team, which reports to the Department for Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP).
There are various schemes initiated by the Government, Central Government, and State governments, for the promotion and growth of supporting entrepreneurs.
An issuer who is willing to start his/her own business may register on www.startupindia.gov.in
- Why choose a startup?
- Working culture can hugely affect our attitude, motivation, and thus, performance. Startups are known for having an innovative and particular working culture.
- Working culture can hugely affect our attitude, motivation, and thus, performance. Startups are known for having an innovative and particular working culture.
- Joining a startup means adopting an ‘out of the box mindset.
- You’re not alone! Startup teams are usually very small, which means they’re very close and aligned, working together to achieve the same goals. You’ll be surrounded by highly hardworking, talented, and ambitious people willing to do the impossible. This is a huge motivation to learn from others and also teach and contribute with your knowledge and experience.
- Startups are known to be home to internationally diverse teams. You’ll find all kinds of coworkers, from all kinds of nationalities, backgrounds, and ideologies. This strong multicultural environment can open your mind beyond work and tasks. It also leads employees to have a global vision.
- You won’t join just one single startup. As startups’ offices are often located inside co-working spaces or hubs, you’ll get to know other teams and professionals from other companies and industries. This is not only an advantage when it comes to networking, but a very fun experience! This can also lead to partnerships between different startups, pushing each other forward to keep growing stronger together.
- A startup’s needs are constantly changing, and teams need to be able to adapt and move fast. You’ll develop new skills, and find yourself doing things you’ve never done before, even if it’s not in the job description. Working for a startup, you’ll understand how the whole company works because all teams and departments work closely.
- Being a startup team member comes with great responsibilities. No matter what your title is, your work will make an impact on the company’s growth and success, this will make you feel like the job you’re doing has an actual purpose and is a huge motivation. Because there are so many things to do, you’ll learn self-management to prioritize your work and get things done. A startup is a young company trying to make its history, and if you fit and believe in the company’s vision, you’ll have career growth opportunities.
- Startups can change your life, even on personal matters. It’s an intense experience, so you’ll inevitably become more proactive and ambitious outside of work too. You’ll be constantly thinking about how to improve things, be more aware of problems and how to solve them and become more open to new cultures and ways of thinking. You’ll also learn to love challenges and even look for them.
- Benefits Provided under Startup India
- Simple process – The government of India has launched a mobile app and a website for easy registration for startups. Anyone interested in setting up a startup can fill up a simple form on the website and upload certain documents. The entire process is completely online.
- Cost reductions -The government also provides lists of facilitators of patents and trademarks. They will provide high-quality Intellectual Property Right Services including fast examination of patents at lower fees. The government will bear all facilitator fees and the startup will bear only the statutory fees. They will enjoy an 80% reduction in the cost of filing patents.
- Easy access to Funds – A 10,000 crore rupees fund is set up by the government to provide funds to the startups as venture capital. The government is also giving guarantees to the lenders to encourage banks and other financial institutions for providing venture capital.
- Tax holiday for 3 Years – Startups will be exempted from income tax for 3 years provided they get a certification from Inter-Ministerial Board (IMB).
- Apply for tenders – Startups can apply for government tenders. They are exempted from the “prior experience/turnover” criteria applicable for normal companies answering to government tenders.
- R & D facilities – Seven new Research Parks will be set up to provide facilities to startups in the R&D sector[1].
[1] IIT Guwahati IIT Hyderabad IIT Kanpur IIT Kharagpur IISc Bangalore IIT Gandhinagar IIT Delhi Creating a collaborative environment between industry and academia through joint research projects and consulting assignments. Creating a self-sustaining and technologically fertile environment. Encouraging and enabling R&D activities and Startups that are aligned to potential needs of the industry. Providing world class infrastructure for R&D activities and incubation. Enabling development of high quality personnel and motivating professional growth for researchers in companies through part time Masters and PhD Programs.
- No time-consuming compliances – Various compliances have been simplified for startups to save time and money. Startups shall be allowed to self-certify compliance (through the Startup mobile app) with 9 labor and 3 environment laws.
- Tax saving for investors – People investing their capital gains in the venture funds set up by the government will get an exemption from capital gains. This will help startups to attract more investors.
- Choose your investor – After this plan, the startups will have an option to choose between the VCs, giving them the liberty to choose their investors.
- Easy exit – In case of exit – A startup can close its business within 90 days from the date of application of winding up.
- Meet other entrepreneurs- The government has proposed to hold 2 startup fests annually both nationally and internationally to enable the various stakeholders of a startup to meet. This will provide huge networking opportunities. Startups are being highly encouraged by the government. The benefits enjoyed by them are immense, which is why more people are setting up startups.
- How do Investors earn returns from investing in Startups?
Investors realize their return on investment from startups through various means of exit. Ideally, the VC firm and the entrepreneur should discuss the various exit options at the beginning of investment negotiations. A well-performing, high-growth startup that also has excellent management and organizational processes is more likely of being exit-ready earlier than other startups.
Venture Capital and Private Equity funds must exit all their investments before the end of the fund’s life. The common exit methods are:
1. Mergers and Acquisitions: The investor may decide to sell the portfolio company to another company in the market.
For example, The $140mn acquisition of RedBus by South African Internet and media giant Naspers and integrating of it with its India arm Ibibo group, presented an exit option for its investors, Seedfund, Inventus Capital Partners, and Helion Venture Partners.
2. IPO: Initial Public Offering is the first time that the stock of a private company is offered to the public. Issued by private companies seeking capital to expand, it is one of the preferred options for investors looking to exit a startup organization.
3. Exit to Financial Investors: Investors may sell their investment to other venture capital or private equity firms
4. Distressed Sale: Under financially stressed times for a startup company, the investors may decide to sell the business to another company or a financial institution
5. Buybacks: Founders of the startup may also buyback their investment from the fund
- Tax examination available to eligible startups under section 80IAC
- An eligible startup will be getting a 100% tax rebate on profit for consecutive 3 years out of the first 10 years since incorporation provided that annual turnover does not exceed Rs. 25 crores in any financial year. This benefit will be available.
- Under The Income Tax Act, 1961, where a Startup (company) receives any consideration for the issue of shares that exceeds the Fair Market Value (FMV) of such shares, such excess consideration is taxable in the hands of the recipient as Income from Other Sources.
- In the context of Startups, where the idea is at a conceptualization or development stage, it is often difficult to determine the FMV of such shares. In the majority of the cases, FMV is also significantly lower than the value at which the capital investment is made. This results in the tax being levied under section 56(2) (viib). Currently, investment by venture capital funds in Startups is exempted from operations of this provision. The same shall be extended to investments made by incubators in the Startups.
- Under The Income Tax Act, 1961, where a Startup (company) receives any consideration for the issue of shares that exceeds the Fair Market Value (FMV) of such shares, such excess consideration is taxable in the hands of the recipient as Income from Other Sources.
- Exemptions provided to startups by the ministry of corporate affairs
A startup is a private company incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013. This complies with the Ministry of Commerce and Industry & Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion Notification released on June 13, 2017. As per the startup notification, a firm is considered a startup if it satisfies the following conditions:
- The firm should be either a private limited company or limited liability or partnership firm. The annual revenue of the company must not exceed 25 crore rupees.
- The firm must be less than seven years old from the date of registering. However, few companies from the Biotechnology segment are provided exceptions until ten years.
- The firm must try to work on innovation, building or enhancing their goods, procedures, and services. It shall adopt a flexible business model with a robust efficiency for job growth and economic growth.
A notification regarding the exemptions available for startups (also the private companies), which would positively aid the newly incorporated companies in carrying out their businesses, was released by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs. Under this notification, few amendments were made to the provisions in the Companies Act, 2013.

- RBI regulations for startups a boost for entrepreneurs/ Benefits to Startups under Atmanirbhar Bharat
The latest development has been the relaxation by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on external commercial borrowing (ECB) by startups, introduced via Circular No. 13 of 27 October 2016.
The RBI has amended the ECB framework from time to time to streamline the process and guidelines for availing of ECB. ECB is currently governed by the RBI’s master direction on external commercial borrowings, trade credit, borrowing, and lending in foreign currency by authorized dealers and persons other than authorized dealers dated 1 January 2016. However, the creation of a parallel relaxed ECB framework specifically for startups is a welcome step that will bolster confidence among startups. Many young entrepreneurs see this as an assurance of an avenue to raise finances without seeking help from foreign venture capitalists (which young Indian promoters have often relied on in the past), and without giving up their crucial stake in the start-up venture.
Via Circular No. 13, the RBI, under its fourth bi-monthly monetary policy statement for the financial year 2016-17, has permitted startups to access loans under the ECB framework up to a limit of US$3 million or equivalent per financial year, either in Indian rupees or any convertible foreign currency or a combination of both. The startup can raise this ECB under the automatic route.
Measures for businesses including MSMEs – These measures would support eligible startups
Rs 3 lakh crore Emergency Working Capital Facility for Businesses, including MSMEs
Rs 20,000 crore Subordinate Debt for Stressed MSMEs.
Rs 50,000 crore Equity infusion for MSMEs through Fund of Funds.
By including this threshold the definition of MSME has been revised and the new definition of MSME is hereunder:
| Type | Investment | Turnover |
|---|---|---|
| Micro | 1 crore | 5 crore |
| Small | 10 crore | 50 crore |
| Medium | 50 crore | 250 crore |
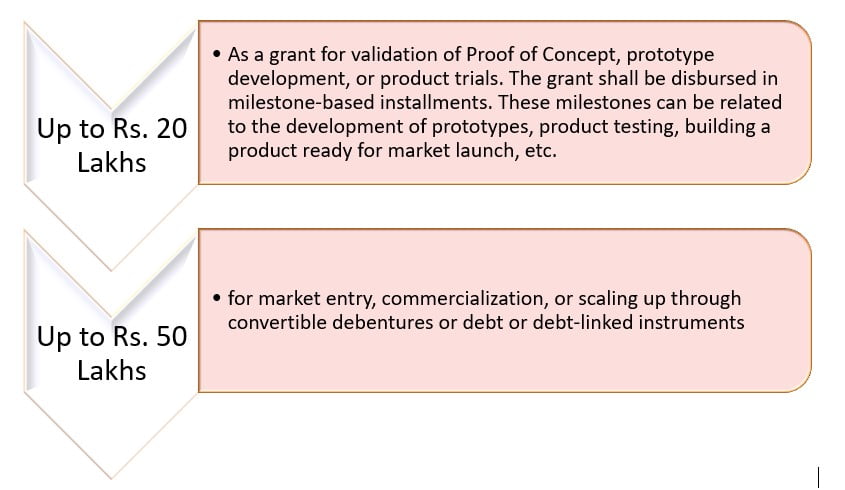
Disbursement of Seed Fund to Startups by Incubators:
Seed Fund to an eligible startup by the incubator shall be disbursed as follows:
- Common Registration Mistakes that Hit Startups Hard
- Choosing the Wrong Legal Structure For Business – A business entity in India can be registered under different formats. You can start your business as a Private Limited Company (PLC), One Person Company (OPC), Limited Liability Partnership Firm (LLP), General Partnership Firm, or Sole Proprietorship Firm. Each entity structure has its own set of pros and cons. The choice you make in terms of entity type can put restrictions with regard on the number of people who can join as owners, fresh capital infusion, etc. and that is why you should acquaint yourself with salient features of each entity structure before taking the plunge.
- Single Founder-One Man Army – If you are a founder and think that you can carry on the business on your own, it is time to RETHINK! As you grow you will need people to bring in expert knowledge, capital, and enterprise skills. Choose an entity structure that allows multiple people to join you as the business grows.
Note: In One Person Company, there can be only one member, however, there can be multiple directors.
- Poor Incentives for Employees Attracting talented individuals is crucial for business growth. Today entities are issuing ESOPs (Employee Stock Option Plans). This way employee gets an ownership feel and aligns his efforts with business goals.
Note: All limited companies can issue ESOPs to attract talent.
- Delay in launching the business
If you have a business plan and it is actionable get it registered under a suitable framework and secure legal protection for your business and co-owners.
Note: The expenses like consultation fees, entertainment expenses, etc incurred during the inception of the business can be claimed as business expenses only after the company has been incorporated.
- Poor Fund Requirement Analysis
Funds form the backbone of a business. Choose a structure that can accommodate capital infusion without many complexities.
Note: An OPC needs to compulsorily convert into a PLC when its capital contribution exceeds Rs. 50 lakh.
- Ignorance About Applicable Tax & Other Government Registration
Multiple Central and State level authorities form policies and regulate business operations. The authorities require businesses to get registered under legislation such as Shop and Establishments Act, Professional Tax Act, etc.
Often entrepreneurs are ignorant about the applicability of particular registration and end up paying heavy fines and penalties for non-compliance.
Brief to various government registrations, like:
- Shop and Establishment License: You need to obtain a separate shop license for each of your business locations such as registered office, branch office, etc.
- IEC: Import and export transactions can be carried out only if you have Import and Export Code.
- GST Registration: It is mandatory for every person engaged in the supply of goods or services in India.
- Professional Tax: It is payable when a person is self-employed or is working for an employer. This tax is deducted and collected by the employer and is applicable only in specific states.
- Employee Provident fund: All establishment employing more than 20 employees comes under the preview of the EPF Act.
Avoid making these registration-related mistakes and move ahead in your Startup journey with confidence. If you have any queries or need expert advice to drop your query at contact@affluence.net.in
[1] Private Limited Company (under The Companies Act, 2013) or a Registered Partnership Firm (under The Indian Partnership Act, 1932) or Limited Liability Partnership (under The Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008)
An entity without a PAN can be registered as a Startup on website. However, it is advised that a valid PAN of the entity is provided at the time of registration.
[2] The Board comprises of the following members:
Joint Secretary, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Convener
Representative of Department of Biotechnology, Member
Representative of Department of Science & Technology, Member
Some FAQS on Startup India.
1. Can a foreigner enter into a partnership under the LLP Act and get that LLP registered with Startup India?
A – Yes, a foreign national can enter into a partnership under the LLP Act and get that LLP registered on our website. It can even get recognized by the DIPP.
2. Can I provide two mobile numbers in the registration form?
A – Only one mobile number and one landline number of the authorized representative of the entity can be provided at the time of registration. The portal and the mobile app would be sending an OTP on the mobile number provided by the user to complete the authentication and registration process.
3. What is the time frame for obtaining a certificate of recognition as a ‘Startup’ in case an entity already exists?
A – The certificate of recognition is issued typically within 2 working days upon successful submission of the application
4. If my startup gets recognized, would I obtain a certificate for it? If yes, would I be able to download the certificate?
A- Yes, if your startup gets recognized, you would be able to download a system-generated verifiable certificate of recognition.
5. How do I register as a Mentor/ Investor on the Hub?
A– Registering a profile on the Startup India website is a fairly simple process:
Simply click on ‘Register’ and fill in the details as required in the registration form. An OTP will be sent to your registered email address, post submitting and your profile will get created.
You will have an option to select your profile type. Select “Enabler” as your persona type, post which you’ll be asked to specify what type of enabler you are. Select mentor/investor in the drop-down box depending on your objective. The profile goes under moderations for 24-48 hours, and once our Quality assurance team has done a preliminary check on your mentor creds, your profile is made live.
6. What is the procedure to claim reimbursement by patent facilitators to services offered to startups?
A– After a patent application is received by the Patent Office, the facilitator shall submit the claim for fees as per the fee schedule given in SIPP Scheme. A letter addressed to the Head of Office of the respective Patent Office, giving details of claimed fee for the drafting of the application and his ID proof as a registered Patent Agent, shall be submitted along with the invoice.
7. What is the age limit for an individual to avail of the startup?
A – In the case of the Startup scheme an Individual must be over the age of 18 years.
Disclaimer: This article has been carefully prepared, but it has been written in general terms and should be seen as broad guidance only. This article cannot be relied upon to cover the specific situation and you should not act, or refrain from acting, upon the information contained therein without obtaining specific professional advice. Please contact Affluence Advisory Private Limited to discuss these matters in the context of your circumstances. Affluence Advisory Private Limited, Its Partners, Directors, Employees, and agents do not accept or assume any liability or duty of care for any loss arising from any action taken or not taken by anyone in reliance on the information in this article or for any decision based on it.