Section 186 of the Companies Act, 2013 (“Act”) deals with loan and investment restrictions imposed on companies. The concerning section provides for the rules and regulations governing a company’s giving of loans, guarantees, or securities and also lays down conditions under which a Company can invest in another Company.
PROVISIONS OF SECTION 186 OF THE COMPANIES ACT, 2013
- The Company shall unless otherwise prescribed, make investments through not more than two layers of investment companies:
Provided that the provisions of this subsection shall not affect-
- a company from acquiring any other company incorporated in a country outside India if such other company has investment subsidiaries beyond two layers as per the laws of such country;
- a subsidiary company from having any investment subsidiary for the purposes of meeting the requirements under any law or under any rule or regulation framed under any law for the time being in force.
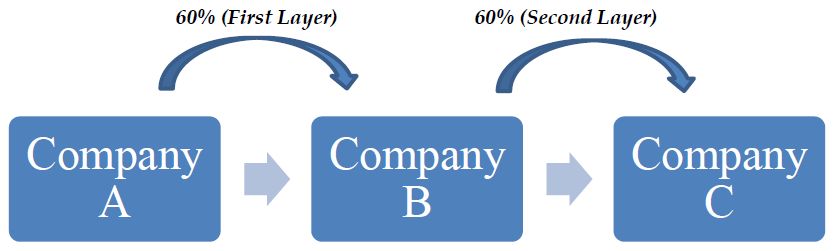
For instance, suppose Company A is the holding company of Company B and Company B is a subsidiary company. Further, company C is a subsidiary company of company B. Thus, when Company A invests in Company B, it is the first layer of investment for Company A. If this investment further flows to Company C, it will be considered as the second layer of investment of holding Company A. This covers two layers of investment for company A and so, it cannot make further layers of investments.
Diagrammatic Presentation:
- No company shall directly or indirectly – Section 186 (2)—

Limit under section 186 (2) is higher of
- 60% of (Paid-up share capital +Free reserve+ Securities Premium) or
- 100% of (Free reserve + Securities Premium)
Note:
- “Person” does not include any individual who is in the employment of the company.
For instance, Mr. X is an employee of Company A. Then, Company A can give a loan to Mr. X and this loan will not be included in the prescribed Limit of Section 186.
- “Body Corporate” includes a company incorporated outside India, but does not include:
- a co-operative society registered under any law relating to co-operative societies; and
- any other body corporate (not being a company as defined in this Act), which the Central Government by notification specify in this behalf;
- “Free Reserves” means those reserves which as per the latest audited balance sheet are
- Free for distribution as dividend and
- Balance to the credit of the securities premium account but shall not include share application money.
- “Securities” includes bonds, debentures, warrants, derivatives, or any other kind of marketable securities. (For a detailed definition kindly refer to the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act of 1956.)
COMPLIANCES UNDER THIS PROVISIONS
- Approval of the Board of Director’s:
The approval of the Board of Directors of the Company (“Board”) shall be obtained through a unanimous resolution passed at a Board Meeting.
Note: Approval of the Board is required irrespective of the amount of Loan, Investment and Guarantee. Every Public Limited Company is required to file E-form MGT-14 within 30 days from the date of passing the Board resolution.
- Approval of the members who vote in favour of the special resolution:
A Special Resolution is required if the total sum of existing and proposed loans, guarantees, investments, or securities exceeds the limit specified in Section 186(2).
Note: The Company is required to file E-form MGT-14 within 30 days from the date of passing special resolution.
However, if the company lends to a Wholly-owned Subsidiary (WOS) or a Joint Venture (JVC), a Holding Company subscribes to acquire securities from its Wholly-Owned Subsidiary, or the company provides a guarantee or securities to its WOS or JVC, no special resolution approval is necessary.
The Special Resolution may contain the total amount authorized by the Board for Loans, Investments, Guarantees, or Securities.
Note: This provision shall not apply to Specify IFSC Company (Public or private) if a company passes a resolution either at the meeting of the Board or by circulation.
- Approval of the Public Financial Institution (PFI):
The approval of the Public Financial Institution (PFI) is required where any term loan is subsisting.
However, prior approval of a PFI shall not be required where the aggregate of the loans and investments so far made, the amount for which guarantee or security so far provided to or in all other bodies corporate, along with the investments, loans, guarantee or security proposed to be made or given does not exceed the limits as specified in sub-section (2) of 186 of the Act. And there is no default in repayment of loan instalments or payment of interest thereon as per terms and conditions of such loan to the PFI.
- Restriction on providing loans on lower rate of interest payable on the Loans:
No loan shall be given under this section at a rate of interest lower than the prevailing yield of 1 year, 3 year, 5 year or 10 year Govt Security closest to the tenor of the loan.
Exception: Nothing contained in this provision shall apply to a company in which 26% or more of the paid-up share capital is held by the Central Govt or one or more State Govt or both in respect of loans provided by such company for funding Industrial Research and Development projects in furtherance of its objects as stated in its MOA.
- Restriction on providing loan, guarantee or security in case of default Committed:
No company which is in default in the repayment of any deposits accepted or in payment of interest thereon, shall give any loan or give any guarantee or provide any security or make an acquisition till such default is subsisting.
- Disclosures in Financial Statements:
The company shall disclose to the members in the financial statement the full particulars of the loans given, investment made or guarantee given or security provided and the purpose for which the loan or guarantee or security is proposed to be utilised by the recipient of the loan or guarantee or security.
- Register of Loans, Investment, Guarantee or Security Provided by the Company:
Every company giving loan or giving a guarantee or providing security or making an acquisition of securities shall, maintain a register in the Form MBP-2 and enter therein separately, the particulars of loans and guarantees given, securities provided, and acquisitions made as aforesaid.
Entries in the register shall be made chronologically in respect of each such transaction within 7 days of making such loan or giving guarantee or providing security or making acquisition.
Also Read: Compliance in the Age of Digital Transformation: Balancing Innovation with Regulation
NON-APPLICABILITY OF SECTION 186
- For the Government Company
- Defense production company owned by the government; and
- Governmental companies other than listed companies, if they obtain approval from the Ministry or Department of CG, which is administratively in charge of them or the State Government, as applicable.
- For the acquisition of shares
To any investment-
- Acquisition by an investment company whose primary business is the acquisition of securities;
- made in shares allotted in pursuance of section 62 (1)(a) or in shares allotted in pursuance of rights issues made by a body corporate;
- made in respect of investment or lending activities, by a NBFC registered with RBI and whose principal business is acquisition of securities.
- For loans, guarantees or security
To any loan made, any guarantee given, or any security provided or any investment made by:
- In the ordinary course of business, a banking company;
- In the ordinary course of business, an insurance company;
- In the ordinary course of business, a housing finance company; and
- A company that provides infrastructure or finances companies
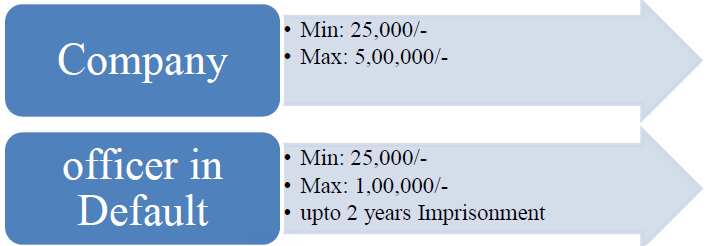
PENALTY
Disclaimer: This article provides general information existing at the time of preparation and we take no responsibility to update it with the subsequent changes in the law. The article is intended as a news update and Affluence Advisory neither assumes nor accepts any responsibility for any loss arising to any person acting or refraining from acting as a result of any material contained in this article. It is recommended that professional advice be taken based on specific facts and circumstances. This article does not substitute the need to refer to the original pronouncement
CLICK HERE DOWNLOAD PDF